Adding Synthetic Hemodynamic Reponses to Data
This example notebook illustrates the functionality in cedalion.sim.synthetic_hrf to create simulated datasets with added activations.
[1]:
# This cells setups the environment when executed in Google Colab.
try:
import google.colab
!curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ibs-lab/cedalion/dev/scripts/colab_setup.py -o colab_setup.py
# Select branch with --branch "branch name" (default is "dev")
%run colab_setup.py
except ImportError:
pass
[2]:
# set this flag to True to enable interactive 3D plots
INTERACTIVE_PLOTS = False
[3]:
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import xarray as xr
import cedalion
import cedalion.dataclasses as cdc
import cedalion.data
import cedalion.geometry.landmarks as cd_landmarks
import cedalion.dot as dot
import cedalion.models.glm as glm
import cedalion.nirs
import cedalion.vis.anatomy
import cedalion.vis.blocks as vbx
import cedalion.sigproc.quality as quality
import cedalion.sim.synthetic_hrf as synhrf
import cedalion.xrutils as xrutils
from cedalion import units
xr.set_options(display_expand_data=False)
if INTERACTIVE_PLOTS:
pv.set_jupyter_backend('server')
else:
pv.set_jupyter_backend('static')
Loading and preprocessing the dataset
This notebook uses a high-density, whole head resting state dataset recorded with a NinjaNIRS 22.
[4]:
rec = cedalion.data.get_nn22_resting_state()
geo3d = rec.geo3d
meas_list = rec._measurement_lists["amp"]
amp = rec["amp"]
amp = amp.pint.dequantify().pint.quantify("V")
display(amp)
<xarray.DataArray (channel: 567, wavelength: 2, time: 3309)> Size: 30MB
[V] 0.0238 0.02385 0.02375 0.02361 0.02364 ... 0.2887 0.2892 0.2897 0.291 0.2923
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 26kB 0.0 0.1112 0.2225 ... 367.8 367.9 368.0
samples (time) int64 26kB 0 1 2 3 4 5 ... 3303 3304 3305 3306 3307 3308
* channel (channel) object 5kB 'S10D87' 'S10D94' ... 'S47D29' 'S5D137'
source (channel) object 5kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S56' 'S47' 'S5'
detector (channel) object 5kB 'D87' 'D94' 'D89' ... 'D129' 'D29' 'D137'
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
Attributes:
data_type_group: unprocessed raw[5]:
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_montage3D(rec["amp"], geo3d)
[6]:
# Select channels which have at least a signal-to-noise ratio of 10
snr_thresh = 10 # the SNR (std/mean) of a channel.
snr, snr_mask = quality.snr(rec["amp"], snr_thresh)
amp_selected, masked_channels = xrutils.apply_mask(
rec["amp"], snr_mask, "drop", "channel"
)
print(f"Removed {len(masked_channels)} channels because of low SNR.")
Removed 22 channels because of low SNR.
[7]:
# Calculate optical density
od = cedalion.nirs.cw.int2od(amp_selected)
Construct headmodel
We load the the Colin27 headmodel, since we need the geometry for image reconstruction.
[8]:
head_ijk = dot.get_standard_headmodel("colin27")
# transform coordinates to a RAS coordinate system
head_ras = head_ijk.apply_transform(head_ijk.t_ijk2ras)
[9]:
display(head_ijk.brain)
display(head_ras.brain)
TrimeshSurface(faces: 29988 vertices: 15002 crs: ijk units: dimensionless vertex_coords: ['parcel'])
TrimeshSurface(faces: 29988 vertices: 15002 crs: mni units: millimeter vertex_coords: ['parcel'])
[10]:
head_ras.landmarks
[10]:
<xarray.DataArray (label: 73, mni: 3)> Size: 2kB
[mm] 0.0045 -118.6 -23.08 -86.08 -19.99 ... -100.4 37.02 49.81 -99.34 21.47
Coordinates:
* label (label) <U3 876B 'Iz' 'LPA' 'RPA' 'Nz' ... 'PO1' 'PO2' 'PO4' 'PO6'
type (label) object 584B PointType.LANDMARK ... PointType.LANDMARK
Dimensions without coordinates: mni[11]:
center_brain = np.mean(head_ras.brain.mesh.vertices, axis=0)
We want to build the synthetic HRFs at C3 and C4 (green dots in the image below)
[12]:
plt_pv = pv.Plotter()
vbx.plot_surface(plt_pv, head_ras.brain, color="#d3a6a1")
vbx.plot_surface(plt_pv, head_ras.scalp, opacity=0.1)
vbx.plot_labeled_points(
plt_pv, head_ras.landmarks.sel(label=["C3", "C4"]), show_labels=True
)
plt_pv.camera.position = (-400, 500,400)
plt_pv.show()
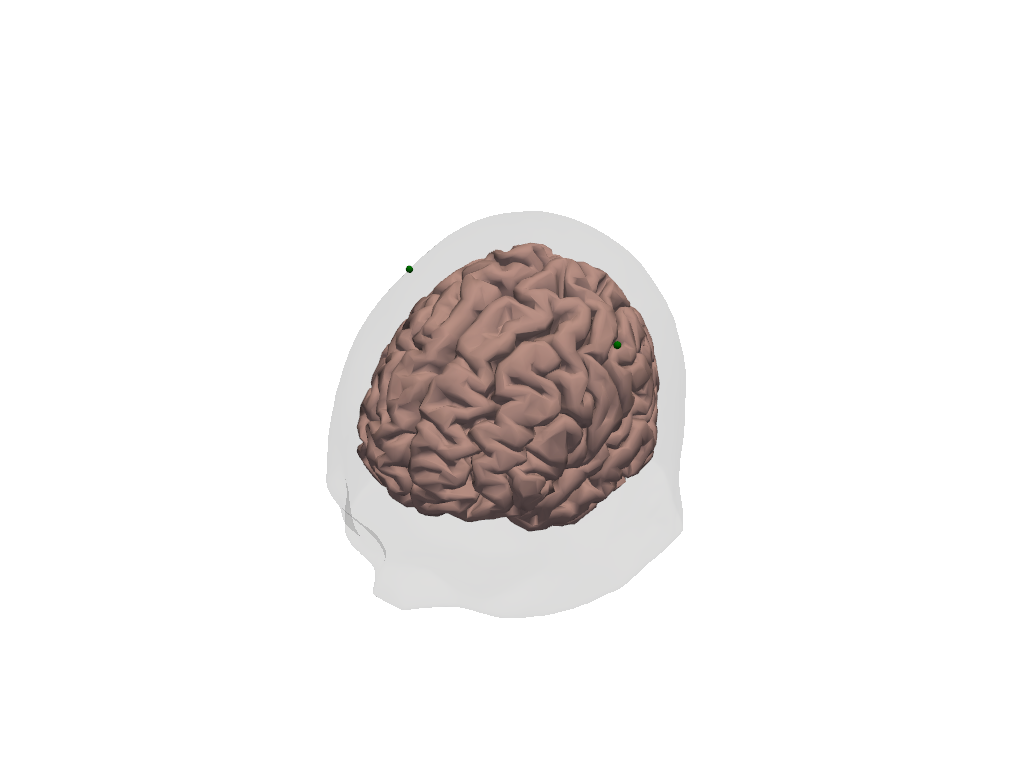
Build spatial activation pattern on brain surface for landmarks C3 and C4
The function build_spatial_activation is used to place a spatial activation pattern on the brain surface. The activation pattern is a Gaussian function of the geodesic distance to a seed vertex. Hence, the size of the activation is determined by the standard deviation of this Gaussian, specified by the parameter spatial_scale. The peak intensity in HbO is determined by the parameter intensity_scale. The intensity of HbR activation is specified relative to the HbO peak intensity. So
if the HbO pattern describes an increase in Hbo then providing a negative factor smaller than 1 yields a decrease in HbR with smaller amplitude. The seed vertex (integer) can be selected as the closest vertex to a given landmark:
[13]:
# obtain the closest vertices to C3 and C4
c3_seed = head_ras.brain.mesh.kdtree.query(head_ras.landmarks.sel(label='C3'))[1]
c4_seed = head_ras.brain.mesh.kdtree.query(head_ras.landmarks.sel(label='C4'))[1]
/opt/miniconda3/envs/cedalion_250922/lib/python3.11/site-packages/xarray/core/variable.py:315: UnitStrippedWarning: The unit of the quantity is stripped when downcasting to ndarray.
data = np.asarray(data)
[14]:
# create the spatial activation
spatial_act = synhrf.build_spatial_activation(
head_ras.brain,
c3_seed,
spatial_scale=2 * cedalion.units.cm,
intensity_scale=1 * units.micromolar,
hbr_scale=-0.4,
)
The resulting DataArray contains an activation value for each vertex and chromophore on the brain surface.
[15]:
display(spatial_act)
<xarray.DataArray (vertex: 15002, chromo: 2)> Size: 240kB [M] 1.115e-28 -4.461e-29 2.003e-29 -8.013e-30 5.23e-30 ... 0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 Coordinates: * chromo (chromo) <U3 24B 'HbO' 'HbR' Dimensions without coordinates: vertex
[16]:
f,ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(10,5))
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_act.sel(chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[0],
camera_pos="C3",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-1,
vmax=+1,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
title=None,
)
ax[0].set_title("HbO")
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_act.sel(chromo="HbR").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[1],
camera_pos="C3",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-1,
vmax=+1,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbR / µM",
title=None,
)
ax[1].set_title("HbR");
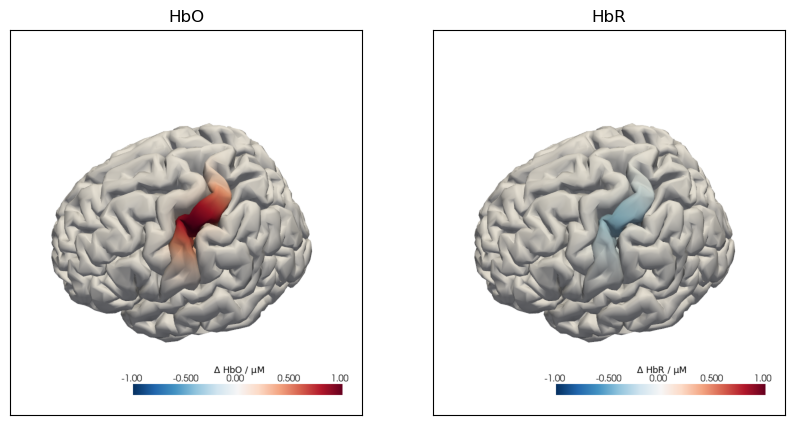
The following plot illustrates the effects of the spatial_scale and intensity_scale parameters:
[17]:
f, ax = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(9, 6))
for i, spatial_scale in enumerate([0.5 * units.cm, 2 * units.cm, 3 * units.cm]):
spatial_act = synhrf.build_spatial_activation(
head_ras.brain,
c3_seed,
spatial_scale=spatial_scale,
intensity_scale=1 * units.micromolar,
hbr_scale=-0.4,
)
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_act.sel(chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[0, i],
camera_pos="C3",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-1,
vmax=+1,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
title=None,
)
ax[0, i].set_title(f"spatial_scale: {spatial_scale.magnitude} cm")
for i, intensity_scale in enumerate(
[
0.5 * units.micromolar,
1.0 * units.micromolar,
2.0 * units.micromolar,
]
):
spatial_act = synhrf.build_spatial_activation(
head_ras.brain,
c3_seed,
spatial_scale=2 * units.cm,
intensity_scale=intensity_scale,
hbr_scale=-0.4,
)
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_act.sel(chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[1, i],
camera_pos="C3",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-2,
vmax=+2,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
title=None,
)
ax[1, i].set_title(f"intensity_scale: {intensity_scale.magnitude} µM")
f.tight_layout()
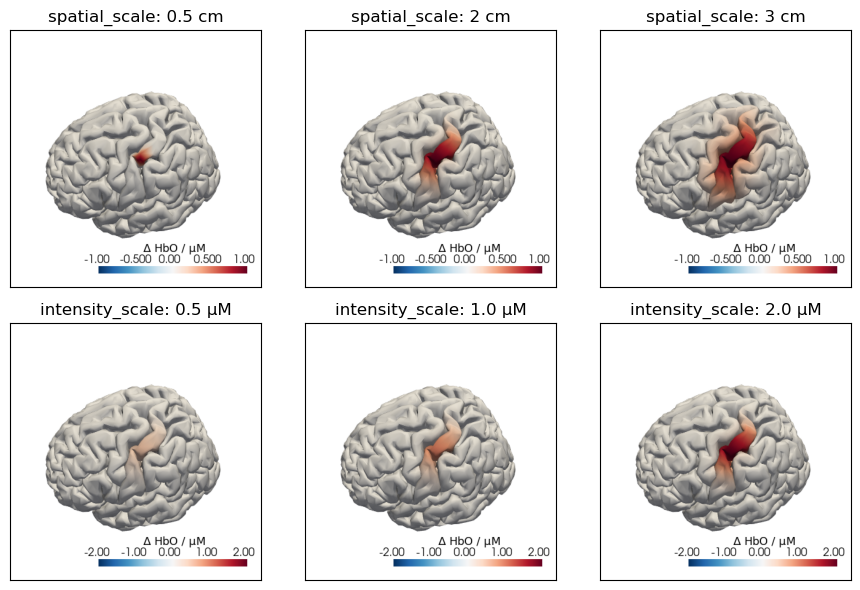
For this example notebook two activations are placed below C3 and C4:
[18]:
spatial_act_c3 = synhrf.build_spatial_activation(
head_ras.brain,
c3_seed,
spatial_scale=2 * cedalion.units.cm,
intensity_scale=1 * units.micromolar,
hbr_scale=-0.4,
)
spatial_act_c4 = synhrf.build_spatial_activation(
head_ras.brain,
c4_seed,
spatial_scale=2 * cedalion.units.cm,
intensity_scale=1 * units.micromolar,
hbr_scale=-0.4,
)
We concatenate the two images for C3 and C4 along dimension trial_type to get a single DataArray with the spatial information for both landmarks.
[19]:
# concatenate the two spatial activations along a new dimension
spatial_imgs = xr.concat(
[spatial_act_c3, spatial_act_c4], dim="trial_type"
).assign_coords(trial_type=["Stim C3", "Stim C4"])
spatial_imgs
[19]:
<xarray.DataArray (trial_type: 2, vertex: 15002, chromo: 2)> Size: 480kB [M] 1.115e-28 -4.461e-29 2.003e-29 ... -2.887e-14 1.427e-21 -5.706e-22 Coordinates: * chromo (chromo) <U3 24B 'HbO' 'HbR' * trial_type (trial_type) <U7 56B 'Stim C3' 'Stim C4' Dimensions without coordinates: vertex
Plots of spatial patterns
Using the helper function cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes, the created activations on the brain surface below C3 and C4 are plotted:
[20]:
f, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(10,5))
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_imgs.sel(trial_type="Stim C3", chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[0],
camera_pos="C3",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-1,
vmax=+1,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
title="C3 Activation",
)
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_imgs.sel(trial_type="Stim C4", chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[1],
camera_pos="C4",
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=-1,
vmax=+1,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
title="C4 Activation",
)
f.tight_layout()
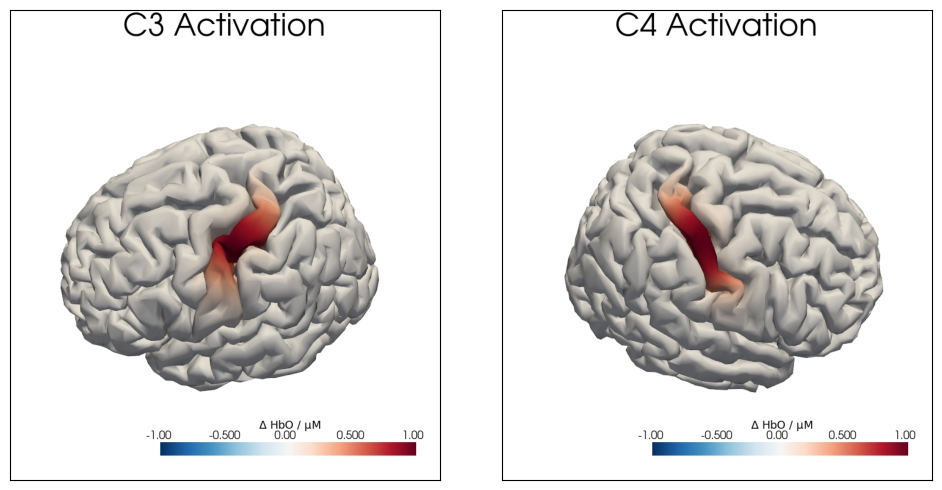
Image Reconstruction
We load the precomputed Adot matrix to be able to map from image to channel space. (For details see image_reconstruction example notebook).
[21]:
Adot = cedalion.data.get_precomputed_sensitivity("nn22_resting", "colin27")
[22]:
# we only consider brain vertices, not scalp and drop pruned channels
Adot_brain = Adot.sel(vertex=Adot.is_brain, channel=od.channel)
Adot_brain
[22]:
<xarray.DataArray (channel: 545, vertex: 15002, wavelength: 2)> Size: 131MB
4.881e-18 4.881e-18 7.405e-18 7.405e-18 ... 0.0001423 1.332e-12 1.332e-12
Coordinates:
parcel (vertex) object 120kB 'VisCent_ExStr_8_LH' ... 'Background+Fr...
is_brain (vertex) bool 15kB True True True True ... True True True True
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D87' 'S10D94' ... 'S47D29' 'S5D137'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D87' 'D94' 'D89' ... 'D129' 'D29' 'D137'
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S56' 'S47' 'S5'
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
Dimensions without coordinates: vertex
Attributes:
units: mmThe forward model and image reconstruction translate between timeseries of different wavelengths in channel space and time series of different chromophores in image space. To this end the image reconstruction operates on stacked arrays in which the dimensions ‘channel’ and ‘wavelength’ are stacked to form a new dimension ‘flat_channel’. Likewise the dimensions ‘vertex’ and ‘chromo’ are stacked as ‘flat_vertex’.
To multiply the spatial image with the sensitivity matrix the spatial image’s vertex and chromo dimensions must be stacked, too.
[23]:
# propagate concentration changes in the brain to optical density
# changes in channel space
spatial_chan = dot.forward_model.image_to_channel_space(
Adot_brain, spatial_imgs, spectrum="prahl"
)
spatial_chan
[23]:
<xarray.DataArray (trial_type: 2, wavelength: 2, channel: 545)> Size: 17kB
[] -1.583e-12 -6.242e-11 -3.406e-11 -2.385e-13 ... 4.92e-06 7.374e-08 5.261e-08
Coordinates:
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D112' 'S10D133' ... 'S9D94' 'S9D96'
* trial_type (trial_type) <U7 56B 'Stim C3' 'Stim C4'
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S9' 'S9' 'S9'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D112' 'D133' 'D135' ... 'D92' 'D94' 'D96'Show the spatial activation in channel space with a scalp plot.
[24]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
# adjust plot size
fig.set_size_inches(12, 6)
cedalion.vis.anatomy.scalp_plot(
od,
rec.geo3d,
spatial_chan.sel(trial_type="Stim C3", wavelength=850),
ax[0],
cmap="YlOrRd",
title="850nm, activation under C3",
vmin=spatial_chan.min().item(),
vmax=spatial_chan.max().item(),
cb_label="max peak amplitude",
)
cedalion.vis.anatomy.scalp_plot(
od,
rec.geo3d,
spatial_chan.sel(trial_type="Stim C4", wavelength=850),
ax[1],
cmap="YlOrRd",
title="850nm, activation under C4",
vmin=spatial_chan.min().item(),
vmax=spatial_chan.max().item(),
cb_label="Max peak amplitude",
)
plt.show()
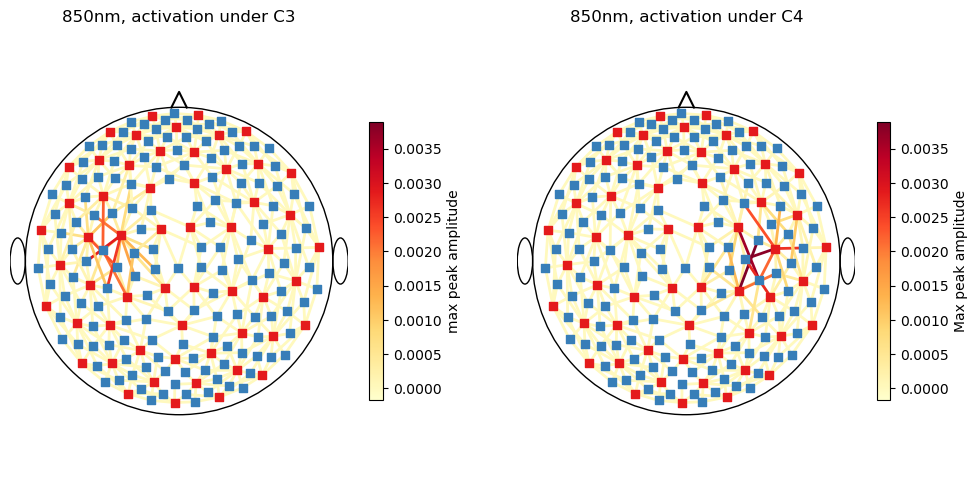
Get top 5 channels for each trial type where synthetic activation is highest
[25]:
roi_chans_c3 = spatial_chan.channel[
spatial_chan.sel(trial_type="Stim C3").max("wavelength").argsort()[-5:].values
].values
roi_chans_c4 = spatial_chan.channel[
spatial_chan.sel(trial_type="Stim C4").max("wavelength").argsort()[-5:].values
].values
Concentration Scale
The activations were simulataed in image space with a peak concentration change of 1 µM in one vertex. The change in optical density in one channel reflects concentration changes in the ensemble of vertices that this channel is sensitive to.
When applying the Beer-Lambert-transformation in channel space, a change in concentration is calculated for each channel. However, the scales of these concentration changes and the concentration changes in single vertices are not the same.
Here, a correction factor is calculated to scale the activation in channel space to 1uM.
[26]:
dpf = xr.DataArray(
[6, 6],
dims="wavelength",
coords={"wavelength": rec["amp"].wavelength},
)
# add time axis with one time point so we can convert to conc
spatial_chan_w_time = spatial_chan.expand_dims("time")
spatial_chan_w_time = spatial_chan_w_time.assign_coords(time=[0])
spatial_chan_w_time.time.attrs["units"] = "second"
display(spatial_chan_w_time)
spatial_chan_conc = cedalion.nirs.cw.od2conc(
spatial_chan_w_time, geo3d, dpf, spectrum="prahl"
)
<xarray.DataArray (time: 1, trial_type: 2, wavelength: 2, channel: 545)> Size: 17kB
[] -1.583e-12 -6.242e-11 -3.406e-11 -2.385e-13 ... 4.92e-06 7.374e-08 5.261e-08
Coordinates:
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D112' 'S10D133' ... 'S9D94' 'S9D96'
* trial_type (trial_type) <U7 56B 'Stim C3' 'Stim C4'
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S9' 'S9' 'S9'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D112' 'D133' 'D135' ... 'D92' 'D94' 'D96'
* time (time) int64 8B 0[27]:
# rescale so that synthetic hrfs add 1 micromolar at peak.
rescale_factor = (1* units.micromolar / spatial_chan_conc.max())
display(rescale_factor)
spatial_chan *= rescale_factor
<xarray.DataArray 'concentration' ()> Size: 8B [] 9.252
[28]:
dpf = xr.DataArray(
[6, 6],
dims="wavelength",
coords={"wavelength": rec["amp"].wavelength},
)
HRFs in channel space
So far the notebook focused on the spatial extent of the activation. To build the temporal HRF model we use the same functionality that generates hrf regressors for the GLM.
First we select a basis function, which defines the temporal shape of the HRF.
[29]:
basis_fct = glm.Gamma(tau=0 * units.s, sigma=3 * units.s, T=3 * units.s)
[30]:
od.time
[30]:
<xarray.DataArray 'time' (time: 3309)> Size: 26kB
0.0 0.1112 0.2225 0.3337 0.445 0.5562 ... 367.5 367.6 367.7 367.8 367.9 368.0
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 26kB 0.0 0.1112 0.2225 0.3337 ... 367.8 367.9 368.0
samples (time) int64 26kB 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... 3303 3304 3305 3306 3307 3308
Attributes:
units: secondA Stim DataFrame, which contains the onset, duration and amplitude of the synthetic HRFs, is created.
[31]:
stim_df = synhrf.build_stim_df(
max_time=od.time.values[-1] * units.seconds,
trial_types=["Stim C3", "Stim C4"],
min_interval=10 * units.seconds,
max_interval=20 * units.seconds,
min_stim_dur = 10 * units.seconds,
max_stim_dur = 10 * units.seconds,
min_stim_value = 1.0,
max_stim_value = 1.0,
order="random",
)
[32]:
stim_df.head()
[32]:
| onset | duration | value | trial_type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15.56 | 10.0 | 1.0 | Stim C4 |
| 1 | 42.80 | 10.0 | 1.0 | Stim C4 |
| 2 | 66.80 | 10.0 | 1.0 | Stim C4 |
| 3 | 89.23 | 10.0 | 1.0 | Stim C3 |
| 4 | 118.42 | 10.0 | 1.0 | Stim C3 |
We can now use our stim dataframe, basis function, and spatial information to create the synthetic HRF timeseries
[33]:
syn_ts = synhrf.build_synthetic_hrf_timeseries(od, stim_df, basis_fct, spatial_chan)
We get a synthetic HRF timeseries for each channel, trial_type and chromo / wavelength
[34]:
syn_ts
[34]:
<xarray.DataArray (trial_type: 2, wavelength: 2, channel: 545, time: 3309)> Size: 58MB
[] -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 ... 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Coordinates:
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D112' 'S10D133' ... 'S9D94' 'S9D96'
* trial_type (trial_type) <U7 56B 'Stim C3' 'Stim C4'
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S9' 'S9' 'S9'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D112' 'D133' 'D135' ... 'D92' 'D94' 'D96'
* time (time) float64 26kB 0.0 0.1112 0.2225 ... 367.8 367.9 368.0Sum the synthetic timeseries over trial_type dimension, so it has the same shape as the resting state data
[35]:
syn_ts_sum = syn_ts.sum(dim='trial_type')
syn_ts_sum
[35]:
<xarray.DataArray (wavelength: 2, channel: 545, time: 3309)> Size: 29MB
[] 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ... 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Coordinates:
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D112' 'S10D133' ... 'S9D94' 'S9D96'
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S9' 'S9' 'S9'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D112' 'D133' 'D135' ... 'D92' 'D94' 'D96'
* time (time) float64 26kB 0.0 0.1112 0.2225 ... 367.8 367.9 368.0Adding HRFs to measured data
Here, the simulated activations are combined with physiological noise by adding the synthetic HRFs to the resting state dataset:
[36]:
# set to false to process only the synth. HRF in the following
ADD_RESTING_STATE = True
if ADD_RESTING_STATE:
od_w_hrf = od + syn_ts_sum
else:
od_w_hrf = syn_ts_sum
od_w_hrf = od_w_hrf.assign_coords(
{
"samples": ("time", od.samples.values),
"time": ("time", od.time.data),
}
)
od_w_hrf = od_w_hrf.pint.quantify({"time": "s"})
Recover the HRFs again
In the following, the added activations should be extracted from the simulated dataset again. To this end, the data is frequency filtered and block averages are calculated.
[37]:
od_w_hrf_filtered = od_w_hrf.cd.freq_filter(fmin=0.02, fmax=0.5, butter_order=4)
[38]:
od_w_hrf_filtered
[38]:
<xarray.DataArray (channel: 545, wavelength: 2, time: 3309)> Size: 29MB
[] 0.002072 0.002634 0.00317 0.003662 ... 0.006999 0.006033 0.004973 0.00387
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 26kB 0.0 0.1112 0.2225 ... 367.8 367.9 368.0
* channel (channel) object 4kB 'S10D87' 'S10D94' ... 'S47D29' 'S5D137'
* wavelength (wavelength) float64 16B 760.0 850.0
samples (time) int64 26kB 0 1 2 3 4 5 ... 3303 3304 3305 3306 3307 3308
source (channel) object 4kB 'S10' 'S10' 'S10' ... 'S56' 'S47' 'S5'
detector (channel) object 4kB 'D87' 'D94' 'D89' ... 'D129' 'D29' 'D137'[39]:
epochs = od_w_hrf_filtered.cd.to_epochs(
stim_df, # stimulus dataframe
["Stim C3", "Stim C4"], # select events
before=5 * units.seconds, # seconds before stimulus
after=20 * units.seconds, # seconds after stimulus
)
# calculate baseline
baseline = epochs.sel(reltime=(epochs.reltime < 0)).mean("reltime")
# subtract baseline
epochs_blcorrected = epochs - baseline
# group trials by trial_type. For each group individually average the epoch dimension
blockaverage = epochs_blcorrected.groupby("trial_type").mean("epoch")
n_roi = roi_chans_c3.size
# show results
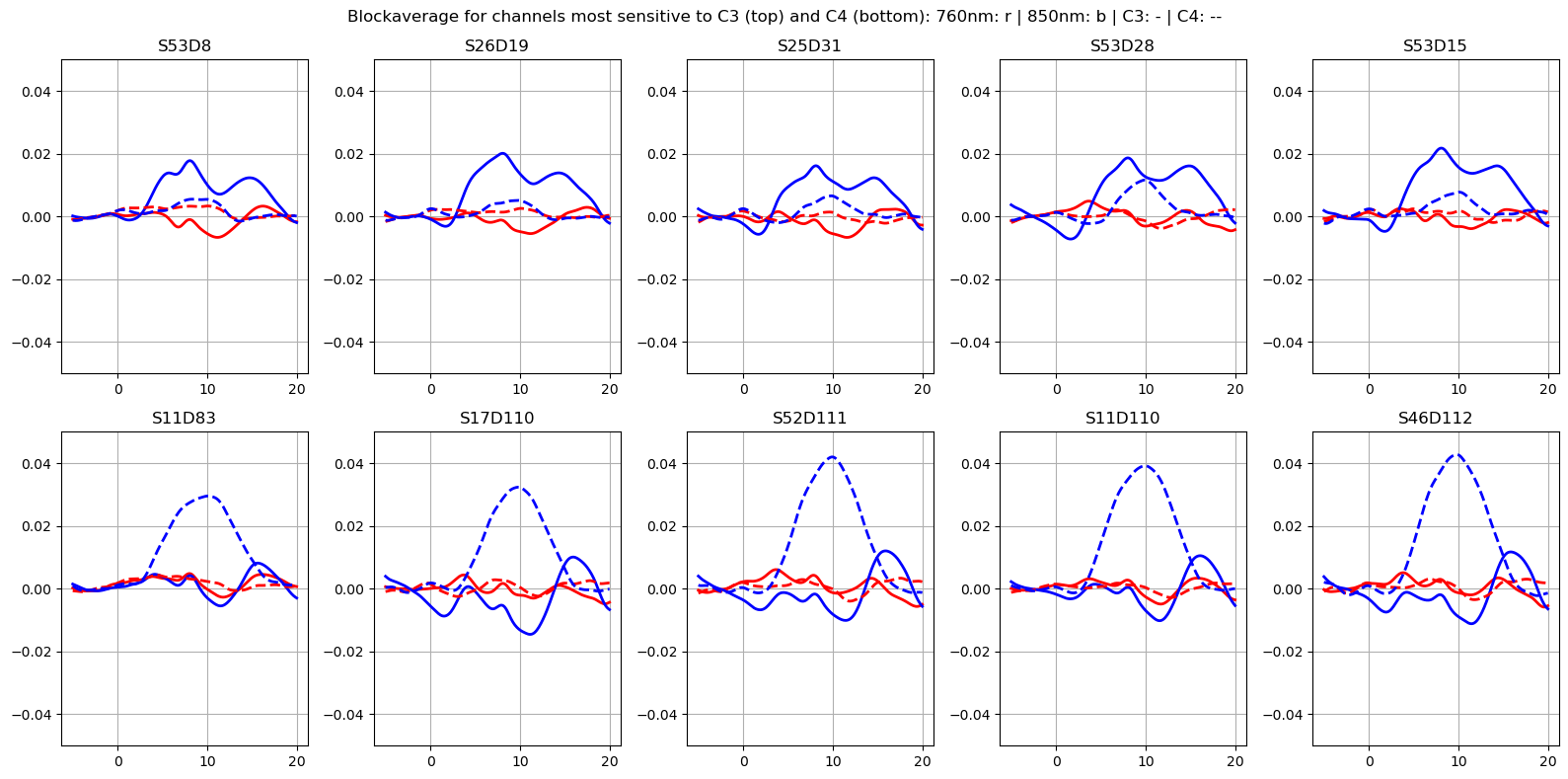
f, ax = plt.subplots(2, n_roi, figsize=(16, 8))
ax = ax.flatten()
for i_ch, ch in enumerate(roi_chans_c3):
for ls, trial_type in zip(["-", "--"], blockaverage.trial_type):
ax[i_ch].plot(
blockaverage.reltime,
blockaverage.sel(wavelength=760, trial_type=trial_type, channel=ch),
"r",
lw=2,
ls=ls,
)
ax[i_ch].plot(
blockaverage.reltime,
blockaverage.sel(wavelength=850, trial_type=trial_type, channel=ch),
"b",
lw=2,
ls=ls,
)
ax[i_ch].grid(1)
ax[i_ch].set_title(ch)
ax[i_ch].set_ylim(-0.05, 0.05)
for i_ch, ch in enumerate(roi_chans_c4):
for ls, trial_type in zip(["-", "--"], blockaverage.trial_type):
ax[i_ch + n_roi].plot(
blockaverage.reltime,
blockaverage.sel(wavelength=760, trial_type=trial_type, channel=ch),
"r",
lw=2,
ls=ls,
)
ax[i_ch + n_roi].plot(
blockaverage.reltime,
blockaverage.sel(wavelength=850, trial_type=trial_type, channel=ch),
"b",
lw=2,
ls=ls,
)
ax[i_ch + n_roi].grid(1)
ax[i_ch + n_roi].set_title(ch)
ax[i_ch + n_roi].set_ylim(-0.05, 0.05)
plt.suptitle(
"Blockaverage for channels most sensitive to C3 (top) and C4 (bottom): 760nm: r | 850nm: b | C3: - | C4: --"
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Map block average back to brain surface
We map our extracted block averages back to the brain surface to visualize the recovered HRFs activation for Stim C3. We can compare it to the synthetic HRF image we created earlier.
[40]:
sbf = dot.GaussianSpatialBasisFunctions(head_ras, Adot, **dot.SBF_GAUSSIANS_DENSE)
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 9680/9680 [00:02<00:00, 3963.73it/s]
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7057/7057 [00:00<00:00, 15563.06it/s]
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 9324/9324 [00:03<00:00, 2522.77it/s]
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1949/1949 [00:00<00:00, 3996.73it/s]
[41]:
recon = dot.ImageRecon(
Adot,
recon_mode="mua2conc",
alpha_meas=0.01,
brain_only=True,
spatial_basis_functions=sbf
)
blockaverage_img = recon.reconstruct(blockaverage)
blockaverage_img
[41]:
<xarray.DataArray (chromo: 2, vertex: 15002, trial_type: 2, reltime: 226)> Size: 108MB
[µM] -0.01188 -0.01567 -0.01816 -0.01941 -0.01946 ... 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Coordinates:
* chromo (chromo) <U3 24B 'HbO' 'HbR'
* reltime (reltime) float64 2kB -4.995 -4.884 -4.773 ... 19.76 19.87 19.98
* trial_type (trial_type) object 16B 'Stim C3' 'Stim C4'
is_brain (vertex) bool 15kB True True True True ... True True True True
parcel (vertex) object 120kB 'VisCent_ExStr_8_LH' ... 'Background+Fr...
Dimensions without coordinates: vertex[42]:
# plot HbO time trace of left and right brain hemisphere during FTapping/Right
for view in ["left_hemi", "right_hemi"]:
trial_type = "Stim C3"
gif_fname = "Ftapping-right" + "_HbO_" + view + ".gif"
hbo = blockaverage_img.sel(chromo="HbO", trial_type=trial_type).pint.dequantify()
hbo_brain = hbo.transpose("vertex", "reltime")
ntimes = hbo.sizes["reltime"]
b = cdc.VTKSurface.from_trimeshsurface(head_ras.brain)
b = pv.wrap(b.mesh)
b["reco_hbo"] = hbo_brain[:, 0] - hbo_brain[:, 0]
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(
b,
scalars="reco_hbo",
cmap="seismic", # 'gist_earth_r',
clim=(-2.5, 2.5),
scalar_bar_args={"title": "HbO / µM"},
smooth_shading=True,
)
tl = lambda tt: f"{trial_type} HbO rel. time: {tt:.3f} s"
time_label = p.add_text(tl(0))
cog = head_ras.brain.vertices.mean("label")
cog = cog.pint.dequantify().values
if view == "left_hemi":
p.camera.position = cog + [-400, 0, 0]
else:
p.camera.position = cog + [400, 0, 0]
p.camera.focal_point = cog
p.camera.up = [0, 0, 1]
p.reset_camera()
p.open_gif(gif_fname)
for i in range(0, ntimes, 3):
b["reco_hbo"] = hbo_brain[:, i] - hbo_brain[:, 0]
time_label.set_text("upper_left", tl(hbo_brain.reltime[i]))
p.write_frame()
p.close()
[43]:
from IPython.display import Image
display(Image(data=open("Ftapping-right_HbO_left_hemi.gif",'rb').read(), format='png'))
display(Image(data=open("Ftapping-right_HbO_right_hemi.gif",'rb').read(), format='png'))
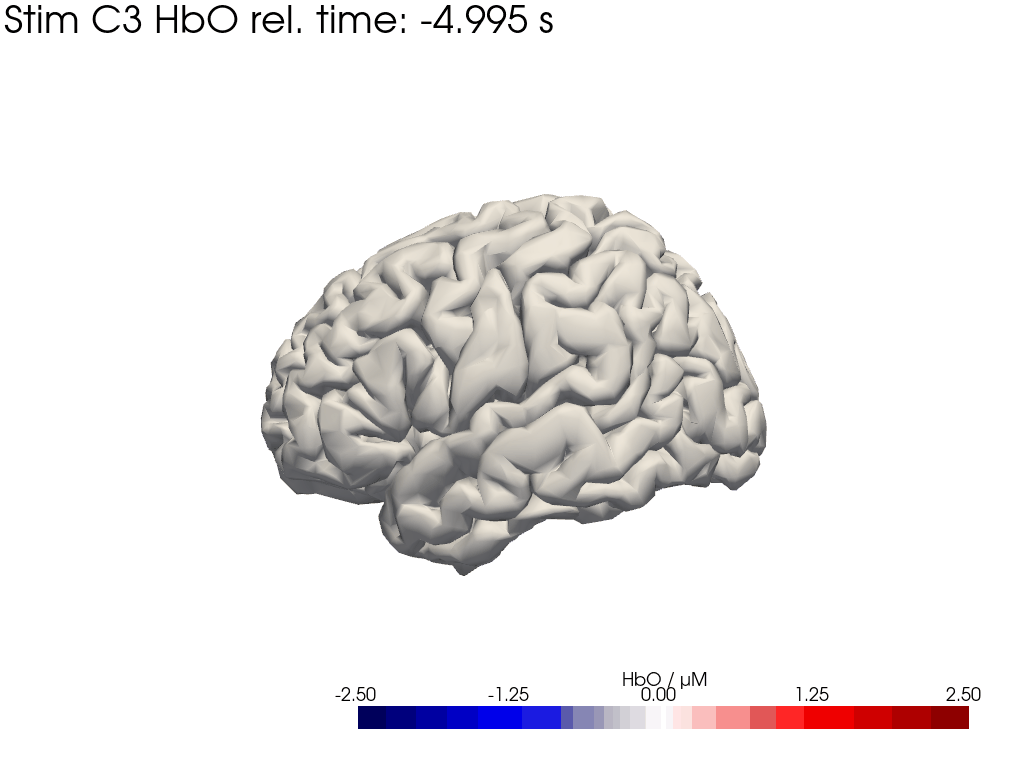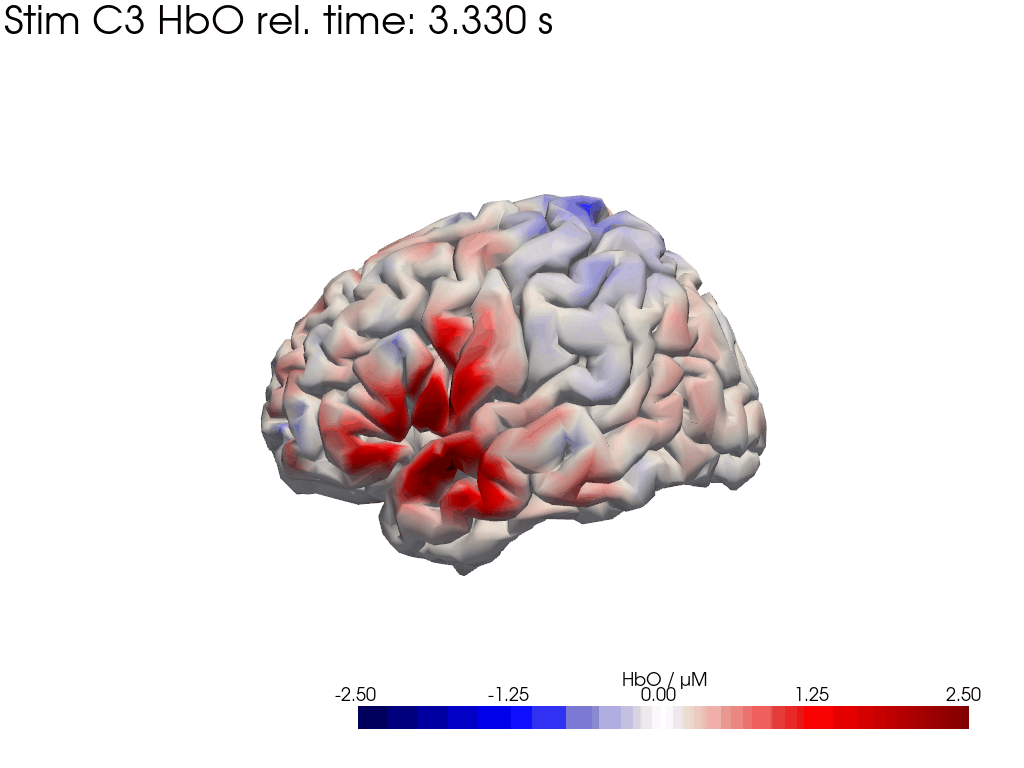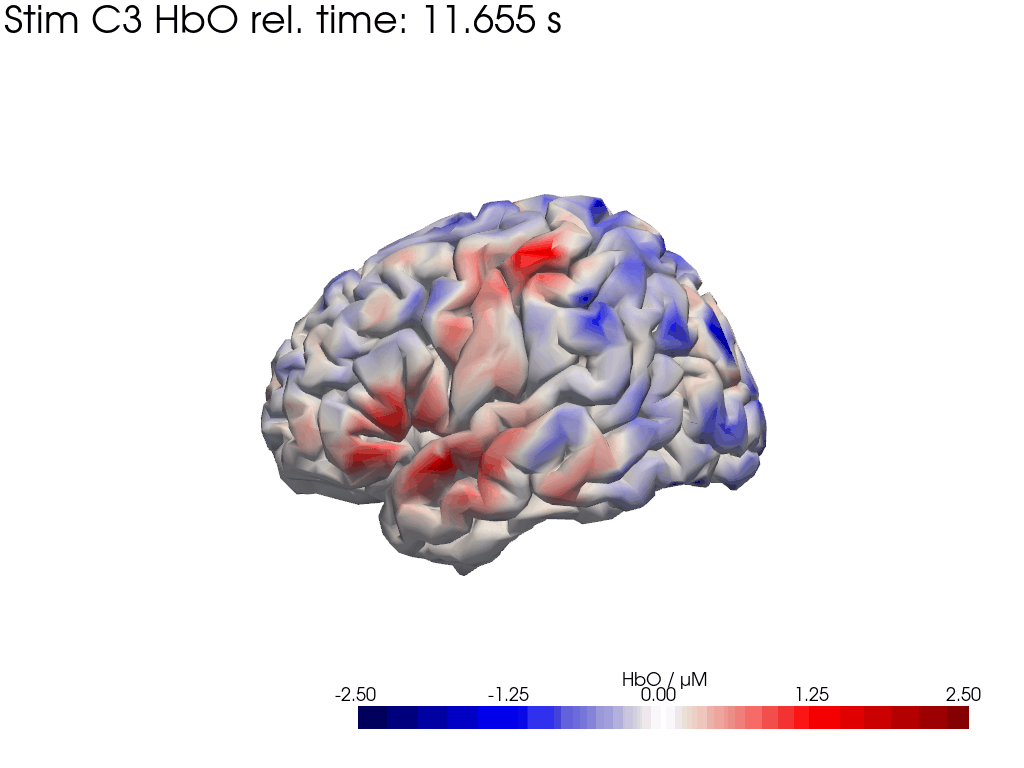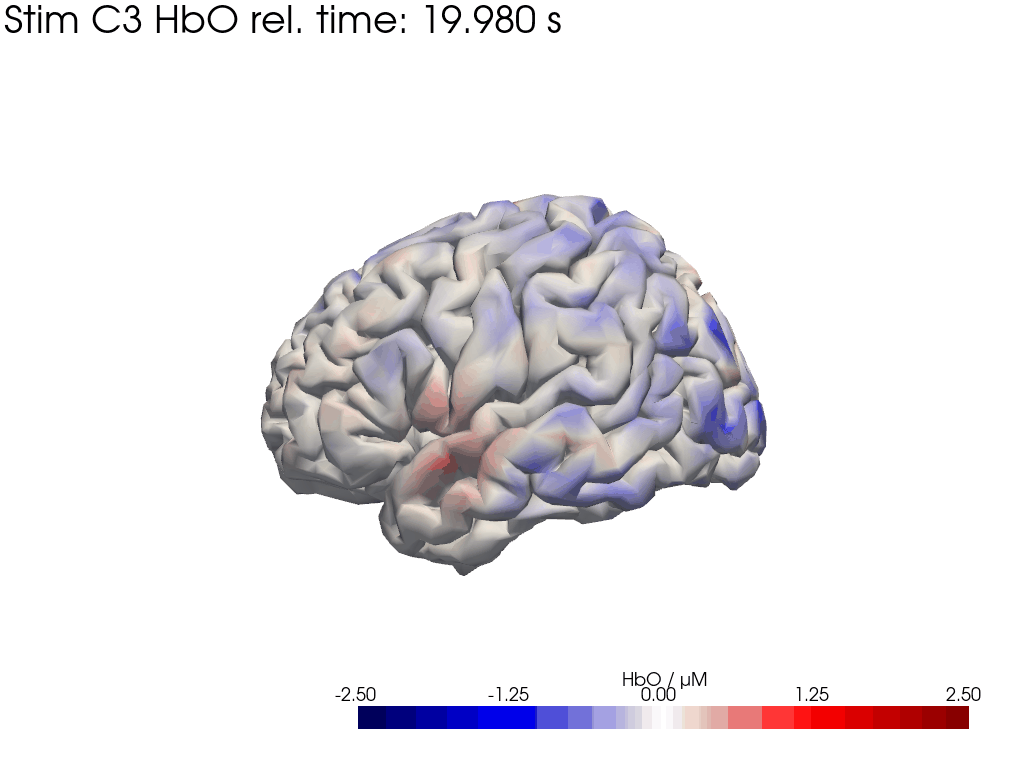
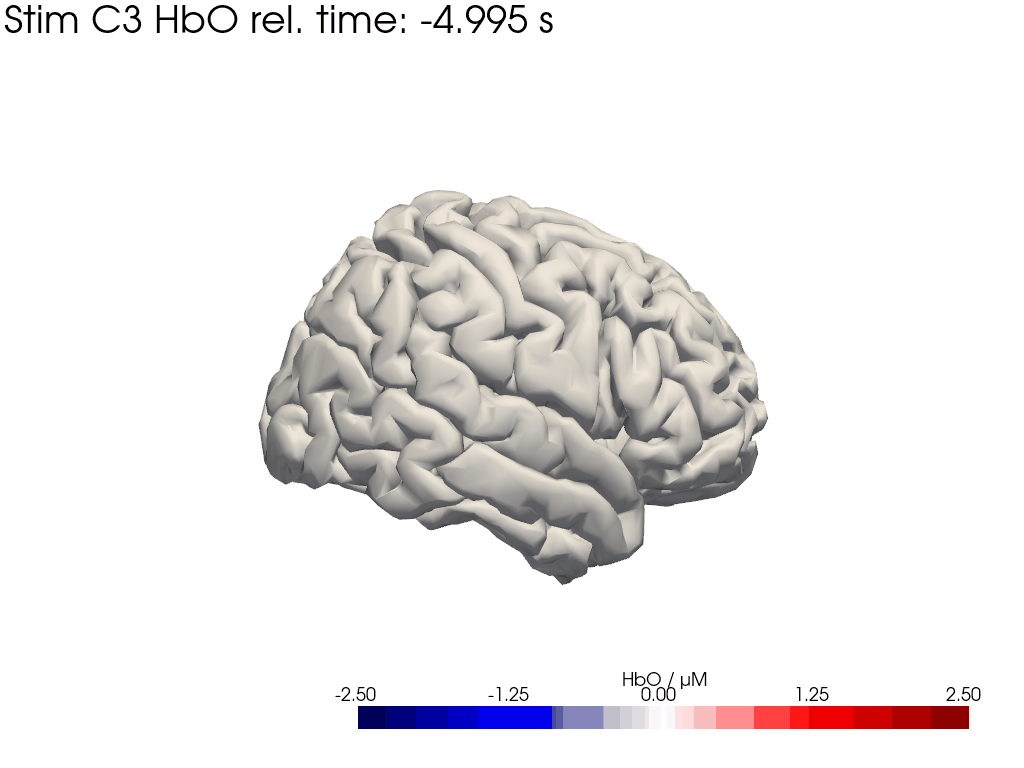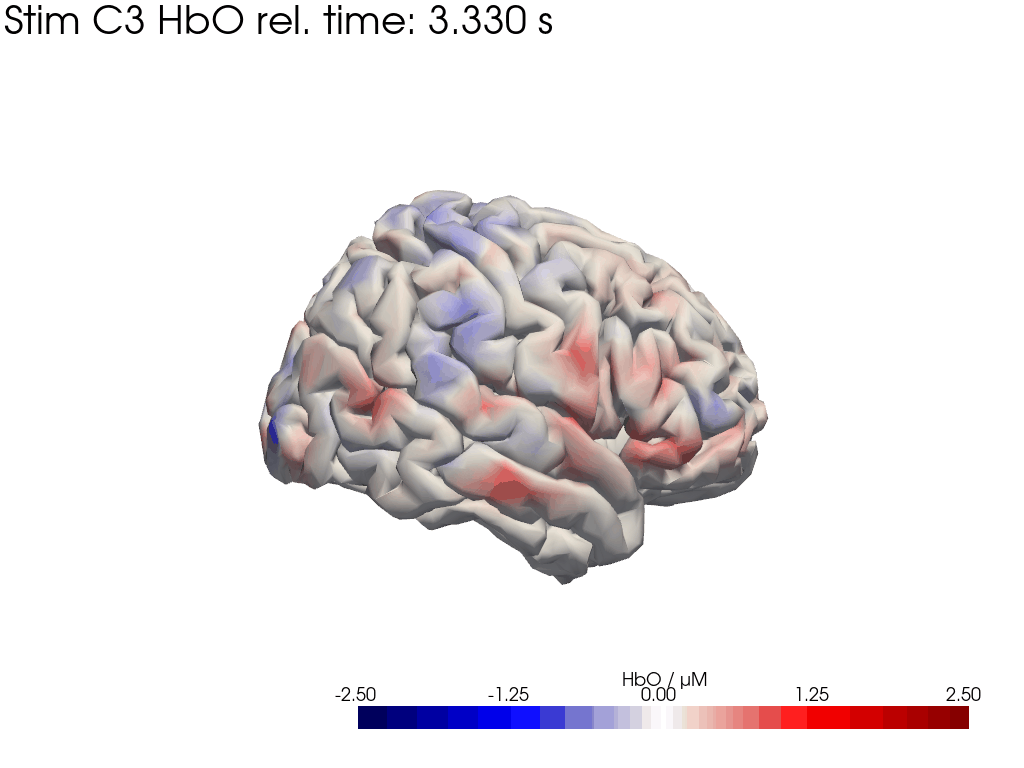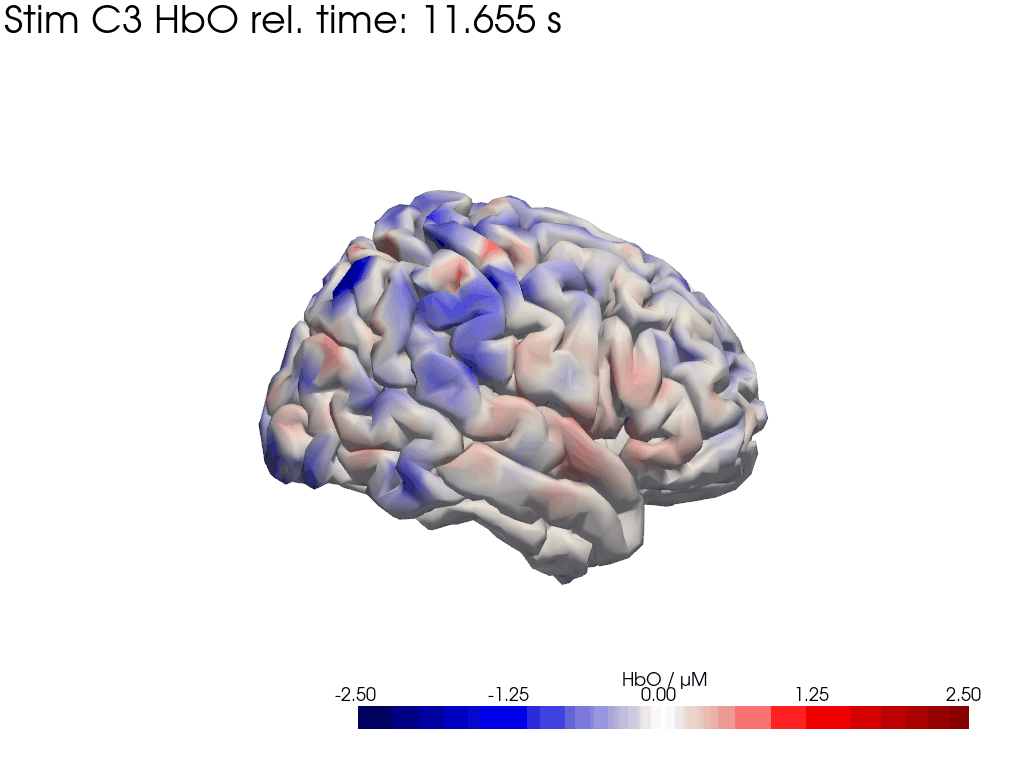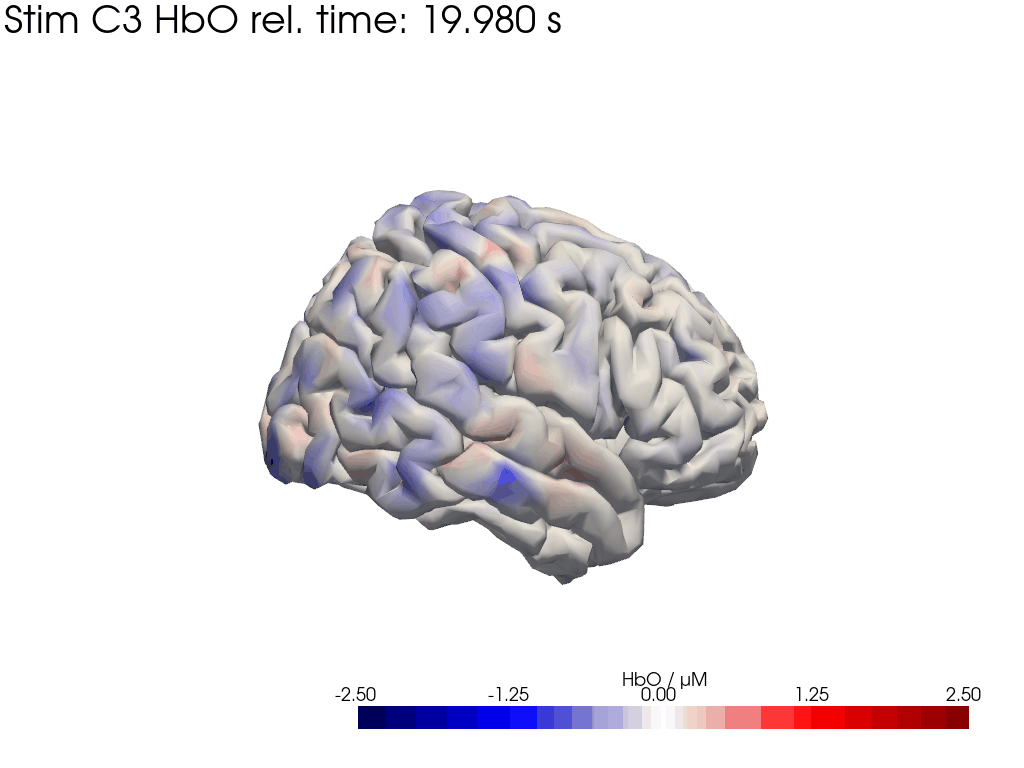
[44]:
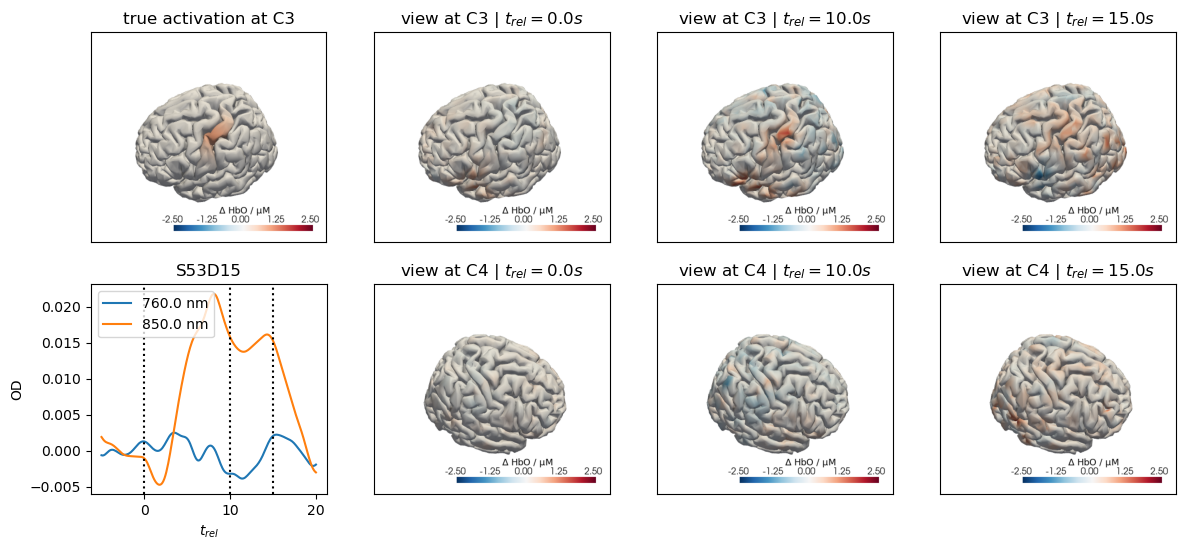
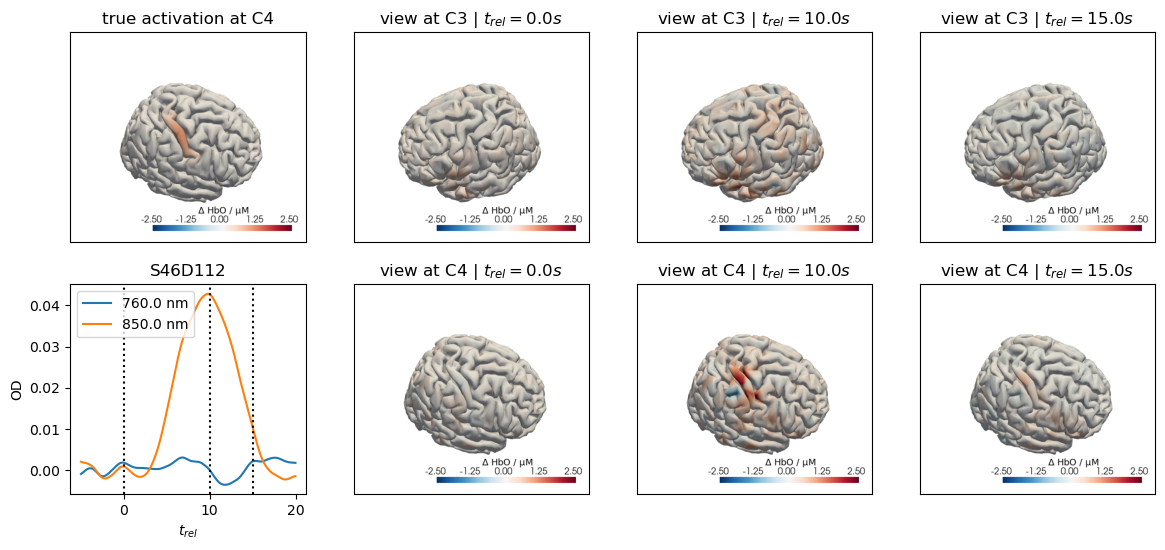
for c, channel in [("C3", roi_chans_c3[-1]), ("C4", roi_chans_c4[-1])]:
trial_type = f"Stim {c}"
f,ax = plt.subplots(2,4, figsize=(14,6))
vmin,vmax = -2.5,2.5
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
spatial_imgs.sel(trial_type=trial_type, chromo="HbO").pint.to("uM"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[0,0],
camera_pos=c,
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=vmin,
vmax=vmax,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
#title=f"{c} Activation",
)
ax[0,0].set_title(f"true activation at {c}")
trels = [0., 10., 15.]
for i_wl, wl in enumerate(blockaverage.wavelength.values):
tmp = blockaverage.sel(
trial_type=trial_type, channel=channel, wavelength=wl
)
ax[1,0].plot(tmp.reltime, tmp, label=f"{wl} nm")
for trel in trels:
ax[1,0].axvline(trel, c="k", ls=":")
ax[1,0].legend(loc="upper left")
ax[1,0].set_xlabel("$t_{rel}$")
ax[1,0].set_ylabel("OD")
ax[1,0].set_title(channel)
for i_col, trel in enumerate(trels, start=1):
for i_row, cam_pos in enumerate(["C3", "C4"]):
cedalion.vis.anatomy.plot_brain_in_axes(
od,
head_ras.landmarks,
blockaverage_img.sel(chromo="HbO", trial_type=trial_type)
.sel(reltime=trel, method="nearest"),
head_ras.brain,
ax[i_row, i_col],
camera_pos=cam_pos,
cmap="RdBu_r",
vmin=vmin,
vmax=vmax,
cb_label=r"$\Delta$ HbO / µM",
#title="$t_{rel}=" + f"{trel:.1f} s$",
)
ax[i_row, i_col].set_title(f"view at {cam_pos} | " + "$t_{rel}=" + f"{trel:.1f} s$")